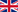
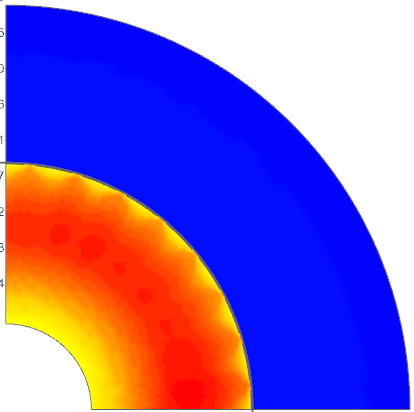
 The Coupled Thermal solution describes the distribution of temperature fields due to losses from electromagnetic solutions or due to applied thermal loads.
The Coupled Thermal solution describes the distribution of temperature fields due to losses from electromagnetic solutions or due to applied thermal loads.
Features
- 3D coupling with several other solution types
- Transient or Static.
- Coupling with frequency domain electromagnetic solutions. E.g. for AC heating over time.
- Temperature dependent material properties.
- Thermal Coupling - Interface Resistance
- Outputs Plot
- Temperature, Temperature Gradient, Temperature Conductive Flux
- Outputs Table
- Temperature Maximum, Temperature Minimum
Examples
| HV Transformer | ||
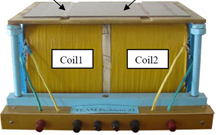 |
Theory and Basics
Formulations
The basis equations:
(1) (lambda grad T, grad T)Ω
+ Dt (Rho Cp grad T, T)Ω
- (0.5 sigma (-Dt a - grad v), T)ΩC (freq. domain)
- (HeatFlux, T)Ωs1
- ((ConvCoeff - AmbiTemp), T)Ωs2
= 0
lambda: thermal conductivity, Rho: density, Cp: thermal capacitance, sigma: electric conductivity, Heatflux: applied heat, ConvCoeff: thermal convection coefficient, AmbiTemp: ambient temperature.